What Muscles does a Stationary Bike Work?
The exercise bike offers a great cardio workout that is generally soft and smooth but it can also be very demanding, especially when the pedaling resistance is set at a very high level, and then have a significant effect on your calves and leg muscles, thighs and buttocks. In addition, cycling gives you well refined muscles since riding on a stationary bike involves a steady effort without jerks. It is therefore ideal if you want to lose weight, tone your legs and get a lean body. We will explain to you what muscles work on a stationary bike and which workout routines are more effective to build muscle and burn calories.
1. What muscles does the exercise bike target?
First and foremost, the exercise bike works out the most important of all muscles, namely your heart! Riding a stationary bike also has many health benefits, increases your endurance and stamina, and is an ideal sport to lose weight. The exercise bike can help you build muscle and target specific parts of your body, which is essential if you want to refine your body. The advantage with the stationary bike is that you can choose and modulate how much you want to work your muscles. The more you increase the pedaling resistance of your bike, the more you work your muscles and develop your muscle mass.
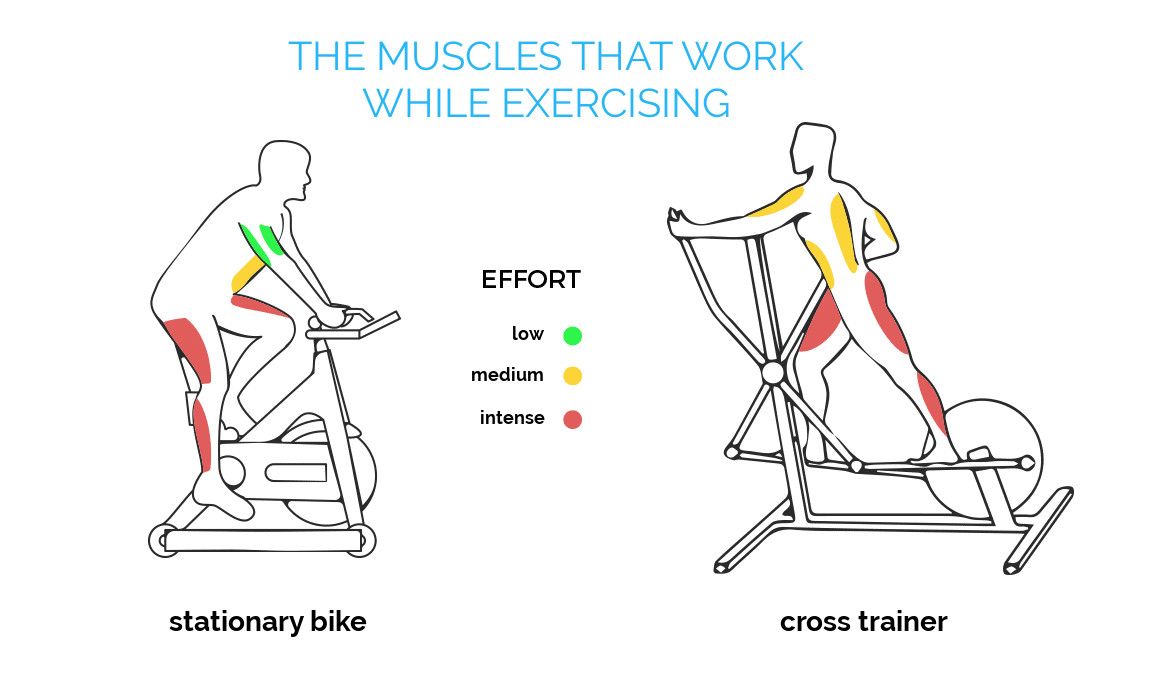
The muscles that work on a stationary bike
Besides the heart, the muscles targeted by the stationary bike are first the leg and thigh muscles as well as the buttocks (or glutes) and then the abdominals and back muscles.
The muscles in the lower part of the body
- the quadriceps and the harmstrings, muscles of the front and the back of the thigh, are constantly working while you are pedaling.
- the gluteal muscles or glutes (large, medium and small buttocks), also called glutes, are also working out when you are pushing the pedals.
- the calf muscles, called triceps sural, located at the back of the leg.
The muscles of the lower limb (in red on the diagram) are mostly working while you are exercising on your stationary bike. The muscles of the upper limb are also working, though to a lesser extent than your legs, thighs, calves and buttocks.
The muscles in the upper part of the body
- The abdominal muscles or abs ensure the posture and the balance of the pelvis and the spine.
- the back muscles, the quadratus lumborum muscle and iliopsoas (in yellow on the diagram), also help to maintain your position and support the spine.
- The biceps and triceps, muscles from the front and back of the arms, allow you to hold the handlebars. The arm muscles (in green on the diagram) work more when you tighten the handlebars, especially when sprinting, or when you are riding out of the saddle with high resistance.
When you are pedaling out of the saddle with high resistance, you put more pressure on your arm muscles (biceps and triceps) and on the muscles of the lower back while your thigh muscles (quadriceps) and your buttocks work less because you are using the weight of your whole body to cycle and thus your legs have less effort to provide.
Make sure you have a good position on your exercise bike and you set the saddle at the right height in order to avoid any problem, tendinitis or muscle pain.
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW: Your muscles need resistance to work! The more you increase the pedaling resistance of your exercise bike, the more strength you need to provide and the more you work your muscles. On the contrary, if the pedaling resistance is too low, you will hardly increase your muscle mass.
-
2. How long does it take to build muscle on the stationary bike?
You are not going to have beautiful thin legs or the perfect buttocks overnight without effort! For that, you need to workout regularly and be constant. You'll see the results after a few weeks. Be patient and persistent and you will see the effect of the exercise bike on your body. If you want to track the evolution of your muscle mass, you can do it with a body fat scale.
In general, you should start seeing the first effects after a few weeks, about 4 to 6 weeks. Your legs, thighs and buttocks are more firm. And your workout should also feel easier and less demanding after 4 to 6 weeks than it was at the very beginning. After 6 weeks, continue working out at this pace and eventually increase the duration and intensity of your exercises, not too much though because doing too much could have a negative impact on your motivation.
After 2 to 3 months, you should clearly see that your legs, your thighs and your buttocks are much more muscular than when you started exercising. Your muscle mass has increased and your fat mass decreased so that your body shape has become more athletic.
Does the exercise bike make your legs and thighs bigger? Don't worry: cycling regularly will not make your legs or your thighs fatter! The exercise bike offers a cardio workout (cardio training) that will tone and refine your legs, thighs and buttocks. If you want to increase the volume of your muscles, then you will have to combine regular training on an exercise bike for 1 hour every day or even more at a very high resistance level with weight training to build muscle. Moreover, the results are (unfortunately) not coming overnight ... you must persevere ;).
-
3. Stationary bike workout routines to build muscle
It all depends on your goal: lose weight (and fat) and tone your muscles or gain muscle mass and volume?
1. To tone and strengthen your legs and thighs muscles and get strong buttocks, you can for instance do a HIIT training on your stationary bike 2 times a week for 30 to 45 minutes, alternating between high intensity phases and recovery phases. Increase the resistance of your bike during the high intensity phases in order to make your muscles work. You should alternate HIIT with cardio workouts of 45 to 60 minutes or more once or twice a week in order to burn fat (aerobic exercise). You will combine fat and weight loss during cardio workout with muscle growth during HIIT training.
2. To muscle your legs and thighs, you can focus almost exclusively on HIIT training with high increases in the pedaling resistance of the bike. For example, you can do 3 to 5 HIIT workouts per week for 20 to 30 minutes.
Here are two exercise bike training plans for gaining muscle and losing weight (N ° 1) and for a greater muscle growth (N ° 2):
Training Plan - N°1
• Combined Cardio & HIIT Workout on Monday (30 to 45 min)
• Cardio Workout at a medium intensity on Thursday (45 to 60 min)
• HIIT Training every Saturday (20-30 min)
Training Plan High Intensity N°2
• HIIT Workout on Monday and Wednesday (20 to 30 min)
• Cardio Workout on Thursday (30 to 60 min)
• HIIT Training on Saturday (30 to 45 min)
The exercise bike is the perfect sports to tone and strengthen legs, thighs and buttocks but also to work the arms, abs and back muscles. Always start your training session with a warm-up at moderate intensity for 5 to 10 minutes and gradually increase the resistance of your stationary bike. The higher the resistance, the more your muscles work. It takes (a little) time to get results, gain muscle and get rid of fat. Perseverance is the key to success ;)
David Anderson is a professional writer with 15 years of experience in the sports and fitness industry. He has been writing about fitness and giving workout tips and advice for the Vescape Fitness Shop since 2016.
RELATED ARTICLES:

10 useful tips to choose the right exercise bike
A squeaking stationary bike, an uncomfortable seat, an exercise bike without resistance... follow our advice and avoid bad surprises in the choice of your exercise bike! Read the article

How to loose weight on a stationary bike?
Does riding a stationary bike help to lose weight? How many calories do you need to burn to lose a pound? How to exercise efficiently to lose fat? All the answers here!