What are the Effects of Exercise on the Brain?
The benefits of exercise and physical activity on the body are well known but did you know that sports and exercise had many effects on the brain as well? Does exercise make us smarter? Happier? Does it improve our memory? Does it help us to age better? These are the questions we are going to address and many more about the unknown exercise benefits on the brain!
1) Does exercise make us happier?
During endurance training or while running, sportsmen or runners have described a state of euphoria. They reported pleasant feelings, an inner harmony, boundless energy or even druglike orgiastic sensations! This is commonly referred to as the « runner’s high » 1 .
This state of euphoria is linked to the release of endorphins, often called the hormone of happiness. During an intense exercise, the release of endorphins raises and can reach up to 5 times its value when we are at rest, which would explain this state of happiness runners and sportsmen feel. If you have already been exercising intensely, you probably know that: after the exercise session, we are in good mood, feel relaxed and peaceful.
Exercise and endorphins. The state of euphoria and inner harmony runners describe is linked to the release of endorphins, commonly called the « hormone of happiness ». Vigorous exercise can stimulate the release of endorphins.
Besides this feeling of well-being, endorphins have other beneficial effects: they reduce stress and anxiety, inhibit pain and may have a positive effect on depression. A team of researchers from the Free University of Amsterdam carried out a study in 2006. They took a sample of 20 000 people and followed them for over 10 years. The people who had been exercising at least 60 minutes per week were on average less anxious, less depressed and less prone to neuroses than those who had not been exercising at all.
Some researchers have speculated that the antidepressant effect of exercise or sports is not solely linked to the secretion of endorphins but also to the production of serotonin. Serotonin is the hormone regulating mood and anxiety. However, it is the secretion of endorphins during exercise that explains the addictive effect of endurance sports like running or cycling!
Exercise and serotonin. Sports and exercise have antidepressant effects which seems to be induced by the secretion of serotonin, the hormone regulating mood and anxiety.
2) Does exercise make us smarter?
A group of Finnish researchers conducted a study in 2005 2 with very interesting experiments on mice doing exercise on a wheel (on average 4-5 km per day! And willingly!). The aim of the study was to see if exercise would induce the creation of new neurons in the brain.
After a month of exercise, the mice were subjected to the Morris maze test to assess their memory. The Morris maze is a swimming pool with different paths and signals helping the mice to find the exit as quickly as possible. The group of mice that had been running regularly on the wheel did perform better and showed better learning abilities.
In addition, the number of neurons in the brain area responsible for learning and memory (cerebral hippocampus) had doubled or tripled in the athletic mice. On the contrary, the number of neurons of the sedentary mice did not increase.
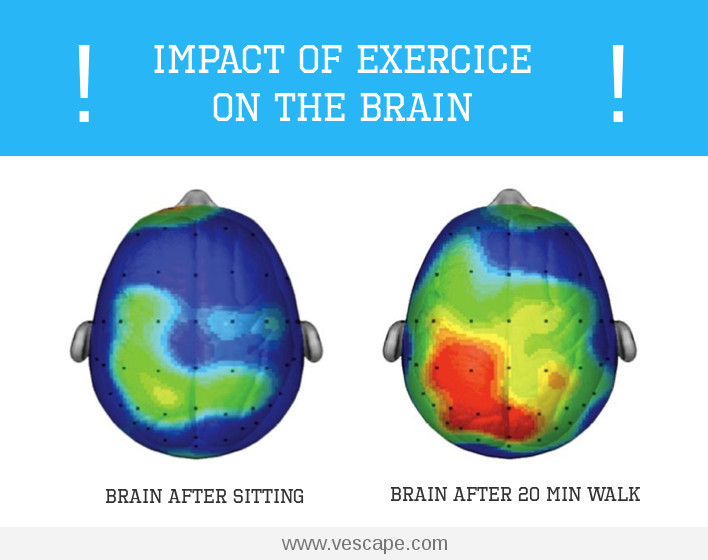
Exercise and neurons. Exercise stimulate the creation of neurons, especially those in the brain area responsible for learning and memory, the cerebral hippocampus.
Another study 3, this time conducted with humans by American researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology in 2014, consisted in examining the relationship between physical activity and memory. These researchers gave students 90 photos to remember. Then they divided the students into two groups: the first group had perform leg strength exercises, while the second group remained seated.
Two days later, the students were asked to recognize the highest number of pictures they could from 180 pictures. The result: the group of students who had completed the training exercises was able to recognize 60% of the pictures while the group who remained seated could remember only 50%! Many other studies have confirmed the positive effects of exercise on learning and memory.
Exercise keeps the brain healthy! With age, learning abilities and memory decline. Sport and exercise help to counteract this decline and improve cognitive abilities. In cognitive tests (learning and memory tests), people exercising regularly obtain better results on average than those not practicing any physical activity. Exercise can therefore help you to train your memory!
3. Does exercise improve sleep quality?
Exercise and physical activity also have an impact on sleep. Sport reduces body temperature and thus provides a better quality of sleep. It is however beneficial only if the physical activity is done between 4 and 8 hours before bedtime. On the contrary, physical activity practiced in the evening in the dark shifts the secretion of melatonin, the sleep hormone, and may be responsible for sleep disorders.
Finally, exercise reduces anxiety which is often a cause of sleep disorders, and thus alleviates sleep disorders anxiety.
Exercise and sleep. Exercise has a beneficial effect on sleep if done during the day but may have the opposite effect if done in the evening.
In 2013, researchers from the Chicago University 4 attempted to demonstrate the benefits of exercise on sleep among people suffering from insomnia. The results were unfortunately not very successful: participants actually did sleep better but not the night after they exercised but only the night of the following day.
However, one causality could be determined: after a bad night's sleep, the participants did not have the same motivation to exercise and training sessions tended to be much shorter ... nice discovery but research does not always give us the results we would like to have!
Conclusion: Exercise has many positive effects on the brain!
The brain benefits of exercise are surprisingly multiple! Regular physical activity and exercise have positive effects on the creation of neurons, on learning, memory, well-being, mood, anxiety, sleep... so exercise is a great way to stay physically and intellectually fit and healthy thanks to the positive effects of exercise on the brain and the body!
However, in order to benefit from these benefits, you should exercise for at least 10 minutes per session. The WHO recommends a minimum of 1h15 of intense physical activity per week.
Thanks to its benefits on the brain and cognitive performance, exercise also reduces the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's but it will be the subject of another article!
OUR ADVICE: Make 2-3 workouts of 30 minutes each per week on your exercise bike to fully enjoy the exercise benefits on the brain!
References:
1. The runner's high: opioidergic mechanisms in the human brain. Boecker H1, Sprenger T, Spilker ME, Henriksen G, Koppenhoefer M, Wagner KJ, Valet M, Berthele A, Tolle TR. Cerebral Cortex. 2008 Nov. 18(11):2523-31. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhn013. Epub 2008 Feb 21.
2. Exercise enhances learning and hippocampal neurogenesis in aged mice. van Praag H1, Shubert T, Zhao C, Gage FH. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2005 Sep 21;25(38):8680-5.
3. A single bout of resistance exercise can enhance episodic memory performance. Weinberg L1, Hasni A2, Shinohara M3, Duarte A4. Acta Psychologica (Amst). 2014 Nov. 153:13-9. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2014.06.011. Epub 2014 Sep 28.
4. Exercise to Improve Sleep in Insomnia: Exploration of the Bidirectional Effects Kelly Glazer Baron, Ph.D., M.P.H., Kathryn J. Reid, Ph.D., and Phyllis C. Zee, M.D., Ph.D. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine. 2013 Aug 15; 9(8): 819–824. Published online 2013 Aug 15. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.2930
RELATED ARTICLES:

Tips & Advice: How to exercise on a stationary bike
Are you sure to have the right position on your exercise bike? Do you know your maximal heart rate? And your optimal heart rate? Did you know that a japanese Professor invented an extremely efficient training method? Discover our tip to make the most out of your exercise... Read the article

10 useful tips to choose the right exercise bike
A squeaking stationary bike, an uncomfortable seat, an exercise bike without resistance... follow our advice and avoid bad surprises in the choice of your exercise bike! Read the article
OUR SELECTION OF EXERCISE BIKES
{products:13,1,9,10}